Creating Influence: Designing a Research Socialization Strategy that Works
Have you ever found yourself in a situation where you’ve conducted extensive user research only to struggle with getting your team and stakeholders to engage with it? If so, you’re not alone. We all derive research insights to drive change and innovation in organizations. However, that's often hard to achieve until our insights are widely shared and integrated into the decision-making processes of other departments. This is where a socialization strategy comes in!
Jenifer Bulcock, a UX Research Consultant and Experience Design Strategist, discussed the importance of a socialization strategy in one of our recent UX Research Munich Community talks. Based on her talk, this article dives deeper into how you can design a socialization strategy that works for your organization. Because, after all, if research is conducted but not used, does it truly exist?
- What is a socialization strategy?
- Dimension 1: Understanding the current state
- People who consume research: Identifying stakeholders and their needs
- Environment and culture: Analyzing corporate structure and behavior
- Dimension 2: Defining the Experience
- Research phases: Ideating with a journey map
- Socialization methods: Evaluating different tactics
- Overview of socialization strategies
- Wrap-up
- Watch recording 🎥
What is a socialization strategy?
Let’s start with a brief definition of what the term socialization strategy means.

Socialization strategy is a deliberate plan for sharing user research insights with relevant stakeholders throughout the organization.
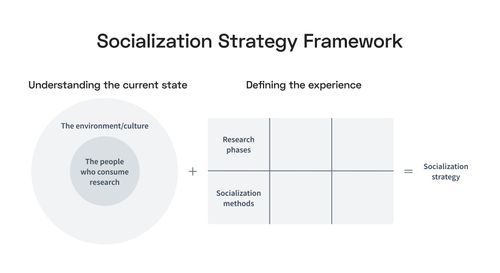
The design of a socialization strategy can be broken down into two dimensions:
Understanding the current state
Stakeholder needs: Identifying and understanding the needs of stakeholders.
Corporate culture: Analyzing the corporate culture and behavior to determine the most effective communication channels and experiences.
Defining the experience
Research phases: Defining the stages and the corresponding goals and deliverables of your research process.
Socialization methods: Determining the most influential socialization methods for each phase.
Using these dimensions, you can create a socialization strategy that delivers the best results. Let’s take a closer look at the different elements of this framework!
Dimension 1: Understanding the current state
As with any well-established design process, it's essential to understand the current state. When it comes to user research, that means identifying the people who consume research and the context in which they operate. Ask yourself who your key stakeholders are, and what environment they exist within. By taking a human-centered design approach and understanding how the company and employees operate, you'll be better positioned to design a socialization strategy that speaks to them.
People who consume research: Identifying stakeholders and their needs
Start by identifying the key stakeholders who can benefit from your user research insights. This may include product managers, designers, developers, marketers, customer support representatives, executives, or other relevant teams.
Once you’ve identified your stakeholders, it’s time to get to know the people in depth! Take the time to understand their specific needs and pain points. What are their goals and objectives? What challenges are they facing? How can your user research insights help them achieve their goals and overcome challenges? By understanding their perspective, you can craft your study and deliverables in the most valuable way and ensure that your work gets traction. Ultimately, if stakeholders see themselves reflected in your research, they’ll be more likely to engage with your findings and use them to inform their decision-making. So, take the time to build connections with your stakeholders and tailor your research approach accordingly.
Environment and culture: Analyzing corporate structure and behavior
The second important aspect to consider is the corporate culture. Start by examining how the organization shares information. What are the typical touchpoints, channels, tools, and behaviors? Is information stored centrally, or is it distributed across different systems? Additionally, consider the extent to which the company operates in a distributed manner or has in-person contact time.
It’s also worth considering whether these communication preferences vary by group, team, or altitude level. By taking a nuanced approach and tailoring your communication strategy to the needs of each stakeholder group, you can ensure that your research insights are effectively shared and utilized throughout the organization.
Dimension 2: Defining the Experience
With a good understanding of your stakeholders and the organizational culture, it's time to start ideating.
Research phases: Ideating with a journey map
Consider how you want your team and stakeholders to experience each phase of the research process, break it down into a journey map with different phases and ensure each has a clear goal and output. This helps create a structured socialization strategy that engages stakeholders and team members at every stage of the process.
#1 Plan
During the planning phase, the goal is to create buy-in and align with your team on goals, timelines, and scope. This helps set expectations and ensures everyone is on the same page before proceeding to the next phase.
#2 Gather / Synthesis
In the gathering and synthesis phase, the focus shifts towards sharing internal findings and building awareness of your process, methods, and insights. This is an opportunity to engage stakeholders and encourage collaboration as you build towards the final deliverable.
#3 Deliver
Eventually, in the delivery phase, you answer the initial questions, build more empathy, validate or invalidate hypotheses, and identify opportunities. This is the phase where you can make recommendations, facilitate the following steps, and present a final deliverable to stakeholders.

Socialization methods: Evaluating different tactics
With your journey map in hand, you can evaluate socialization methods. Consider factors such as content density, synchronicity, and shelf life.
#1 Content density
Content density is an important factor to consider when presenting user research findings. Remember that higher-level stakeholders may not have the same appetite for content-dense presentations as those lower down in the organization.

To cater to your audience's needs, use the Bite, Snack, and Meal framework to categorize your content. Bites are small quotes or insights, snacks are larger summaries, and meals are more in-depth reports.
#2 Synchronous vs. asynchronous
Consider whether to share your findings synchronously or asynchronously. Synchronous sharing allows for in-person discussion and context-building, which can be helpful for team internalization. Asynchronous sharing may be necessary for teams that are dispersed across time zones or have limited availability, and it also allows for a wider audience reach. You could also consider recording a presentation and making it available to everyone in the organization.
#3 Shelf life
The shelf life of your socialization materials is also an essential factor to consider. If your study ties into an overarching company and business strategy, it may be necessary to have a longer shelf life. In contrast, quick status updates may not need to be as findable in the future. You can break up your content based on this determination.
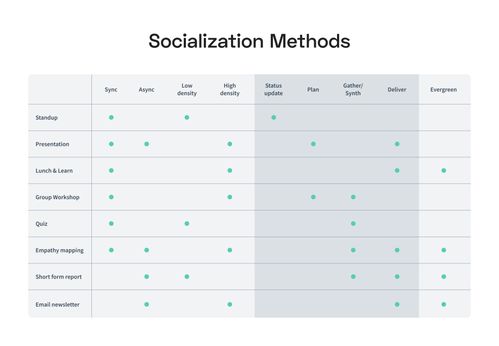
Overview of socialization strategies
As your socialization strategy takes shape, it's important to keep in mind the different dimensions we've discussed - stakeholder needs, company culture, consumption preferences, and journey phases. Match these dimensions with various socialization methods, as shown in the table below. The gray columns demonstrate the related culture and consumption preferences, and the purple columns represent the different stages of the journey. The Evergreen column helps you consider the longevity of your content.
This way, you can select a few socialization tactics that cater to different interested parties at varying levels and altitudes, particularly when working on a large study or with multiple stakeholders.
Wrap-up
Creating influence with user research requires more than just producing comprehensive research reports. You must ensure that your insights are widely shared and integrated into decision-making processes across the organization. Understanding the stakeholders with their respective needs and defining the most effective communication channels and experiences enables you to develop a deliberate socialization strategy that works for your organization. Follow these tips to ensure you're on the right track:
Identify stakeholders and understand their needs
Analyze the company culture and behavior
Define the phases within your research process
Evaluate the different socialization methods
Watch recording 🎥
This article is based on a talk by Jenifer Bulcock, UX Research Consultant and Experience Design Strategist, at the UX Research Meetup in April 2023. You can watch the full video here:
/f/99166/2554x1328/dc2d4d04e2/screenshot-2023-05-11-at-14-39-00.png)